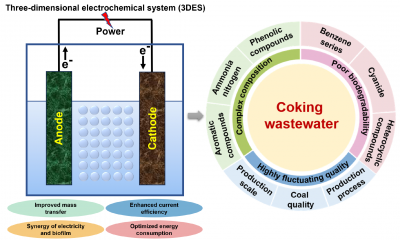
A team of researchers from Anhui Science and Technology University and East China Normal University has released a pivotal review focused on the innovative Three-Dimensional Electrochemical System (3DES) designed for treating coking wastewater. This comprehensive study was published in the journal Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, specifically in Volume 19, Issue 9.
Coking wastewater, a byproduct of the coal coking process, poses significant environmental challenges due to its high levels of pollutants. The review outlines how the 3DES technology addresses these issues effectively. The authors detail the system’s mechanisms and its potential to significantly reduce harmful substances in wastewater, thus making it a critical advancement in environmental engineering.
Key Features and Benefits of 3DES
The 3DES operates by utilizing a three-dimensional electrode configuration that enhances electrochemical reactions. This design not only improves the efficiency of the treatment process but also reduces energy consumption compared to traditional systems. The review emphasizes that this innovative approach can lead to a more sustainable method for managing coking wastewater.
Moreover, the authors present a detailed analysis of various studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of 3DES in degrading toxic compounds commonly found in coking wastewater. By improving pollutant removal rates, the system could play a vital role in protecting water resources and public health.
The review also discusses the economic implications of implementing the 3DES technology. The authors suggest that while the initial investment may be substantial, the long-term benefits, including reduced environmental remediation costs and compliance with stricter regulations, make it a viable option for industries dealing with coking wastewater.
Future Directions and Implications
Looking ahead, the researchers advocate for further studies to optimize the 3DES technology. They highlight the need for pilot projects to validate its effectiveness in real-world applications. Additionally, collaboration between academic institutions and industry stakeholders could accelerate the adoption of this innovative wastewater treatment solution.
By addressing both environmental and economic concerns, the 3DES technology stands out as a promising advancement in wastewater treatment. The findings of this review not only contribute to the academic discussion but also provide a roadmap for industries seeking sustainable practices in wastewater management.
As industries increasingly face pressure to reduce their environmental impact, the insights provided by this comprehensive review could be instrumental in guiding future innovations in wastewater treatment technologies.