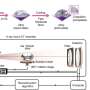
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have developed an advanced imaging technique that allows for the observation of metal crystals growing within liquid metal. This innovative approach has significant implications for enhancing hydrogen production, a key component in the transition to sustainable energy sources. The findings were published in March 2024, marking a notable advancement in materials science.
The process resembles the formation of sugar crystals in a cooling solution. When sugar is dissolved in hot water and the mixture cools, pure sugar crystals emerge, leaving impurities behind. This phenomenon is now being applied to the growth of metal crystals, which can be monitored in real-time using the new imaging technique.
The research team utilized advanced imaging methods to capture the intricate details of crystal growth as it occurs. By observing the dynamics of this process, scientists can gain insights into improving the efficiency of hydrogen production. Hydrogen is increasingly seen as a clean energy source, especially in fuel cells and other applications.
The ability to visualize the growth of nanocrystals in liquid metal opens up new avenues for material design and optimization. The researchers believe that this technique could lead to enhanced catalytic processes that are vital for hydrogen production.
Understanding the conditions that facilitate the growth of these crystals will allow scientists to engineer better catalysts. This advancement could potentially increase the yield of hydrogen produced from various sources, thereby contributing to a greener energy landscape.
In practical terms, the implications of this research extend beyond the laboratory. As countries around the world strive to meet their climate goals, improving hydrogen production efficiency becomes crucial. The transition to hydrogen as a primary energy source could significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
The techniques developed by the research team represent a convergence of materials science, chemistry, and engineering. By merging these disciplines, they have created a framework that not only enhances our understanding of crystal growth but also provides actionable insights for real-world applications.
As the global community increasingly prioritizes sustainability, research initiatives like this one are essential. The findings from the University of California, Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory highlight the importance of innovation in addressing climate change and energy challenges.
This breakthrough serves as a reminder of the potential that lies within scientific research to drive meaningful change in energy production. With continued investment and exploration in this field, the dream of a hydrogen-powered future may become a reality sooner than anticipated.