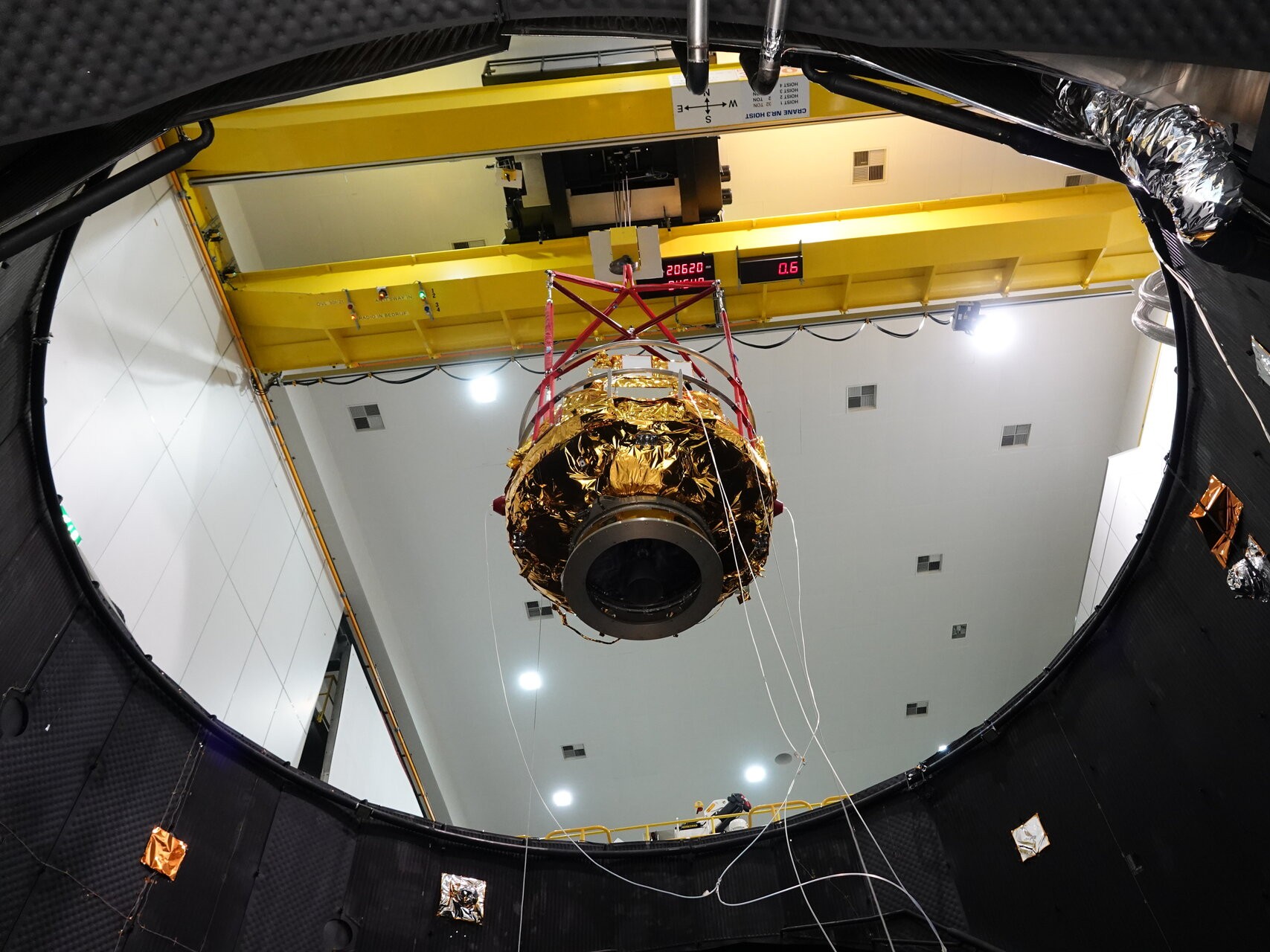
The European Space Agency (ESA) has announced a groundbreaking mission aimed at providing the first comprehensive understanding of how Earth responds to radiation from the Sun. The initiative, set for launch in 2025, will employ advanced technology to gather critical data that could significantly enhance our knowledge of solar impacts.
The mission will utilize the Solar Orbiter, a sophisticated spacecraft designed to study the Sun up close. This project represents a collaborative effort between ESA and NASA, reflecting the importance of international cooperation in space exploration. With the Solar Orbiter’s unique capabilities, researchers expect to gain insights into solar phenomena, which can influence Earth’s atmosphere and climate.
Understanding the Sun’s radiation is vital for predicting its effects on satellite communications, power grids, and even climate patterns. The data collected during this mission will help scientists assess the risks associated with solar storms, which can disrupt technology and pose hazards to astronauts in space.
Collaboration and Technology
The Solar Orbiter will feature an array of instruments that can measure solar radiation and magnetic fields. This will allow scientists to observe solar activity in real-time, providing a clearer picture of how solar emissions interact with Earth’s magnetic field. The mission will also include a series of flybys, notably close encounters with Venus, to gather additional data on the influence of solar radiation on different planetary atmospheres.
ESA officials emphasize the significance of this mission in enhancing our understanding of space weather. According to ESA’s Director of Science, Carlo R. G. T. de L’Isle, “This mission is not just about the Sun; it’s about understanding the broader implications for life on Earth.”
The collaboration between ESA and NASA is expected to amplify the mission’s impact. NASA’s involvement will bring additional expertise and resources, ensuring a thorough investigation of solar dynamics. The project underscores the shared commitment to advancing knowledge about our solar system and its effects on Earth.
Implications for the Future
The research outcomes from this mission could have far-reaching implications. Insights gained may lead to improved forecasting models for solar storms, enhancing preparedness for potential disruptions. Additionally, the findings could inform future space missions, particularly those involving human travel to the Moon and Mars.
As humanity continues to explore the cosmos, understanding the Sun’s behavior remains crucial. This mission stands as a testament to the ongoing quest for knowledge and the importance of partnerships in tackling complex scientific questions.
With the launch slated for 2025, anticipation builds within the scientific community. The Solar Orbiter is poised to deliver unprecedented data that may transform our understanding of solar interactions and their impact on Earth.