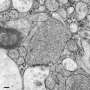
A team at Johns Hopkins Medicine has successfully employed a novel “zap-and-freeze” technique to visualize the communication between brain cells in living tissue from both mice and humans. This groundbreaking advancement offers unprecedented insights into the intricate processes of neuronal interaction, which have remained largely elusive until now.
The researchers managed to capture real-time communication among neurons, revealing how these cells transmit signals to one another. Using this innovative method, they can observe the dynamics of synaptic connections as they occur. This research could pave the way for enhanced understanding of various neurological conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Details of the Technique
The “zap-and-freeze” technique combines rapid electrical stimulation with cryogenic preservation to halt cellular activity instantaneously. This allows scientists to capture high-resolution images of neuronal communication without the interference of ongoing biological processes. The team’s findings highlight the potential of this method to uncover the fundamental mechanisms that govern brain function.
According to the researchers, the ability to visualize brain activity in real time can significantly advance our understanding of how neurons interact. Traditional methods of studying brain cells often involve post-mortem tissue analysis, which does not provide the live-action insights necessary to fully comprehend the complexities of brain communication.
Implications for Future Research
This advancement not only enhances our understanding of neuronal behavior but also holds promise for future therapeutic strategies. By gaining insights into how brain cells communicate, researchers can begin to identify potential targets for intervention in various neurological conditions. The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest; they could influence the development of treatments for diseases that affect millions worldwide.
The study, published in December 2023, emphasizes the vital role that innovative technologies play in neuroscience research. The team at Johns Hopkins Medicine continues to explore the possibilities of their findings, aiming to push the boundaries of what is currently known about brain function and communication.
As the field of neuroscience evolves, the integration of cutting-edge techniques like the “zap-and-freeze” method will undoubtedly contribute to a deeper understanding of the human brain and its intricate network of communications. This research represents a significant step forward in unraveling the mysteries of brain function and offers hope for future developments in treating neurological disorders.