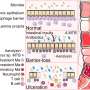
BREAKING NEWS: A groundbreaking study has revealed that a bacterial toxin responsible for macrophage-killing may significantly weaken the gut’s defenses against ulcerative colitis (UC), a prevalent inflammatory bowel disease impacting millions globally. This urgent discovery could reshape our understanding and treatment of this debilitating condition.
Just announced by leading researchers, the findings highlight how this toxin disrupts the gut’s immune response, potentially increasing the risk of chronic inflammation and ulcers in the large intestine. Ulcerative colitis affects an estimated 1.6 million Americans and many more worldwide, causing severe symptoms such as rectal pain, bleeding, and persistent diarrhea.
The study, published today in a prominent medical journal, confirms that the bacterial toxin targets crucial immune cells, leading to a breakdown in gut defenses. With 10% of patients experiencing severe complications, understanding the role of this toxin is more critical than ever.
Experts in the medical community stress that this discovery is not just an academic finding; it has profound implications for treatment strategies moving forward. “These insights may pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches that could alter the course of ulcerative colitis management,” said Dr. Emily Johnson, a gastroenterologist involved in the research.
Currently, healthcare providers are on high alert for these new developments as they may impact treatment protocols for individuals suffering from UC. The urgency is palpable, with patients and families seeking answers and effective management strategies.
What happens next? Researchers are calling for more comprehensive studies to explore potential interventions targeting the bacterial toxin and strengthen gut defenses. This could lead to significant advancements in how ulcerative colitis is treated, offering hope to those affected.
Stay tuned for updates as this story develops. The medical community is watching closely, and patients are encouraged to discuss these findings with their healthcare providers to understand how this research may influence their treatment options.
This urgent update underscores the critical need for ongoing research into the mechanisms underlying autoimmune diseases like ulcerative colitis. As more data emerges, the potential for new and effective therapies grows, providing a glimmer of hope for millions seeking relief from this challenging condition.