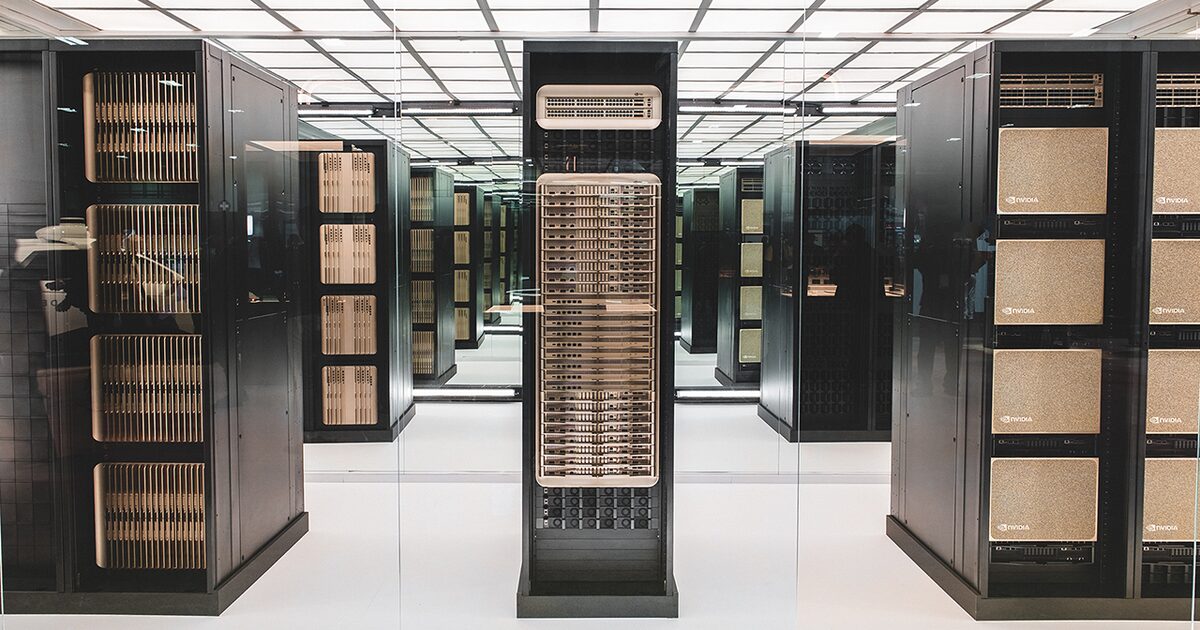
UPDATE: The big four cloud giants are racing to enhance AI inference performance by integrating Nvidia’s Dynamo into their services. This urgent move, announced earlier today, leverages Nvidia’s new Kubernetes-based API, streamlining complex orchestration tasks and boosting efficiency for demanding workloads.
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) are all implementing Dynamo to power their AI initiatives. This development comes at a critical time as the demand for AI capabilities skyrockets worldwide.
Nvidia’s Dynamo is now integrated into managed Kubernetes services, significantly enhancing performance for multi-node inference loads. For instance, AWS is utilizing Dynamo to accelerate inference for customers engaged in generative AI workloads. Notably, it has been integrated with Amazon’s Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) to facilitate efficient scaling for Kubernetes both on AWS and on-premises.
Meanwhile, Google Cloud is employing Dynamo to optimize large language model (LLM) inference on its powerful AI Hypercomputer platform. Microsoft Azure is harnessing this technology to enhance multi-node LLM inference, particularly on its advanced GB200-v6 virtual machines. Azure’s GB300 v6 has set new performance records, pushing the boundaries of inference speeds.
Additionally, OCI is utilizing Nvidia’s Dynamo to support multi-node LLM inferencing on its Superclusters. These high-performance computing clusters are already equipped with cutting-edge networking technology, offering 400 Gb/s connections between GPUs.
Nvidia’s launch of Grove, an open-source Kubernetes API, further enhances this landscape. Grove simplifies the orchestration of workloads across thousands of GPUs, transforming intricate processes into manageable Kubernetes pods. This innovation is available as a modular component within Dynamo or separately via GitHub.
As AI inference becomes increasingly distributed, many hyperscalers are expanding their capabilities by building out robust distributed data centers. These include interconnected facilities like AWS’s Rainier site and Microsoft’s ambitious Fairwater project, which spans hundreds of miles.
Notably, the adoption of Nvidia’s platform is not limited to the big four. Nebius, a European neocloud provider, is leveraging Dynamo to support AI workloads for major clients like Meta and Microsoft. As a growing ecosystem partner, Nebius aims to revolutionize AI capabilities in Europe.
“As AI inference becomes increasingly distributed, the combination of Kubernetes and Nvidia Dynamo with Grove simplifies how developers build and scale intelligent applications,” stated Shruti Koparkar, senior manager of product marketing for AI inference at Nvidia.
With these exciting developments, the cloud computing landscape is set to undergo rapid transformation, enhancing the speed and efficiency of AI applications across various industries. As companies and developers alike prepare for a new era of AI capabilities, the integration of Nvidia’s Dynamo is a game-changer that could redefine how intelligent applications are built and deployed.
Stay tuned for more updates as this story develops, and watch for the impact of these technologies on the future of AI and cloud computing.